Introduction
A new era of affordable and ecologically sustainable mobility options is being ushered in by the electrification of transportation, or eMobility. eMobility controls, an advanced ecosystem of technologies that optimize, monitor, and regulate many elements of electric cars (EVs) and the infrastructure that supports their charging, are at the center of this change. Although eMobility controls have enabled advancements, they also bring several difficulties as well as exciting prospects for the future.
This blog explores the issues that eMobility controls are currently confronting as well as the trends that will shape eMobility in the future.
1. Emobility Controls Challenges
Standardization and Interoperability
A wide range of players make up the eMobility ecosystem, including charging station operators, automakers, and energy suppliers. One of the biggest challenges in eMobility is ensuring that numerous components communicate and work together seamlessly. However, platform integration becomes even more difficult due to the lack of well-defined communication protocols. As a result, inefficiencies arise, leading to user frustration and a fragmented experience. Therefore, to build a truly integrated eMobility ecosystem, it is essential to develop common protocols that enable efficient and reliable device communication.
- Cybersecurity Concerns: As eMobility systems become more interconnected and reliant on data sharing, the risk of cyberattacks also increases. Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in eMobility controls to gain unauthorized access to vehicles or charging infrastructure. Therefore, it is crucial to implement strong cybersecurity measures to protect user information and maintain the integrity of both infrastructure and vehicle systems. To achieve this, real-time threat monitoring, multi-factor authentication, and encryption are some of the key solutions that should be in place.
- Optimization and Management of Energy: Finding the perfect balance between efficacy and efficiency is still a major challenge, even with the developments in eMobility controllers intended to optimize energy distribution and consumption. This calls for the use of sophisticated algorithms and predictive analytics to account for a variety of factors, including:
- Dynamic driving conditions.
- Driver behavior.
- Renewable energy availability.
- To guarantee effective energy use without sacrificing performance, these variables need to be controlled in real-time.
2. Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
An integral part of sustainable mobility is using renewable energy to charge EVs. However, there are many obstacles in the way of incorporating renewable energy sources like wind and solar into the eMobility ecosystem. Because these energy sources are erratic and sporadic, sophisticated energy management systems are needed to
- Make sure the grid is stable.
- Handle energy storage devices well.
- The demand for charging and energy generation should be balanced.
Implementing Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology
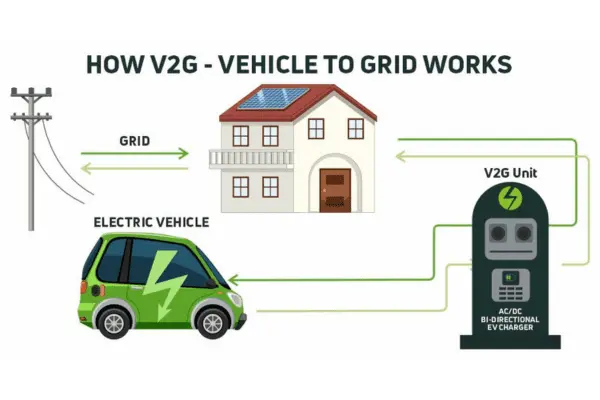
EVs can function as mobile energy storage devices thanks to V2G technology, which helps stabilize the grid and returns energy to it when needed. However, there are infrastructure, legal, and technical barriers to the broad use of V2G. To create the frameworks that allow for smooth bidirectional energy transfer, automakers, utilities, and legislators must work together.
3. Upcoming Developments in eMobility Controls
As advanced machine learning and predictive analytics continue to evolve, the future of mobility will become increasingly intelligent and data-driven. Consequently, these advancements will enable more efficient transportation systems, enhanced safety features, and improved user experiences. Furthermore, real-time data processing and AI-driven decision-making will optimize vehicle performance and traffic management. Ultimately, this technological evolution will not only enhance efficiency and performance but also pave the way for smarter, more sustainable mobility solutions.
eMobility controls are about to undergo a revolution thanks to machine learning and predictive analytics. These technologies can do the following by examining past data, driving trends, and outside variables:
- Optimize the use of energy.
- Make accurate maintenance demand predictions.
- Arrange billing according to cost-effectiveness and energy availability.
- This development will improve EVs’ usability and operational efficiency.
- Intelligent Energy Management
- More advanced energy management strategies that combine real-time data will be incorporated into future eMobility controllers, including:
- patterns of traffic.
- weather.
- variations in grid load.
- eMobility systems will process this data to maximize energy efficiency, lower charging expenses, and enhance the driving experience in general.
4. Autonomous Parking and Charging
Autonomous EVs will have the following capabilities:
- Navigating to charging stations.
- Positioning themselves for optimal energy transfer.
- starting and finishing the charging procedure without assistance from a person.
- This invention will improve the charging infrastructure’s efficiency and streamline the user experience.
5. Integration of Wireless Charging
For EVs, wireless charging is emerging as a practical and efficient solution. As this technology continues to evolve, future eMobility controllers will play a crucial role in:
- ensuring exact alignment to transfer energy.
- keeping an eye on wireless charging solutions to ensure effectiveness.
- combining with car management programs to ensure smooth functioning.
- Blockchain Technology for Safe Transactions
For eMobility transactions, blockchain technology provides enhanced security, transparency, and trust. In particular, it ensures that data remains tamper-proof and transactions are verifiable. Some of its key applications include:
- Secure charging session authentication.
- enabling energy trade amongst peers.
- utilizing decentralized ledgers to streamline billing procedures.
- This will improve the user experience while addressing cybersecurity issues.
6. Optimization of Fleet Management

eMobility controls will develop to assist fleet management as electric vehicles progressively supplant conventional fleet vehicles. These remedies will:
- Schedule charging and routing as efficiently as possible.
- Watch how much energy is being consumed.
- Lower operating expenses while increasing productivity.
- Businesses implementing EVs will need fleet management solutions to ensure efficient and economical operations.
Conclusion
At the vanguard of the electrification revolution, eMobility controls enable the smooth functioning of electric vehicles and the infrastructure supporting their charging. The future is incredibly promising, even despite obstacles like interoperability, cybersecurity, energy management, and the incorporation of renewable energy. Advancements in blockchain technology, wireless charging, intelligent automation, and predictive analytics will completely transform the eMobility environment.
To successfully overcome these obstacles and capitalize on emerging trends, stakeholders—including automakers, energy suppliers, and legislators—must work together. Furthermore, as the mobility sector continues to develop, eMobility controls will be essential in shaping a networked, efficient, and sustainable transportation environment.
Reach out to us at info@dorleco.com to learn more about our exceptional VCU products, CAN Keypads, CAN Displays, and EV software services, or to explore our expertise in VCU architecture, components, and software development for battery-specific applications.


