Introduction
An age of completely automated driving has been made possible by Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), which have completely transformed the automotive sector. These state-of-the-art technologies greatly improve overall security, driving comfort, and vehicle safety. It is impossible to overestimate the importance of ADAS system implementation, nevertheless, because mistakes or malfunctions could have negative effects. As a result, thorough testing and validation are essential to guaranteeing these systems operate safely and dependably.
This blog explores the fundamental elements of ADAS testing and validation, offering perspectives on the approaches, difficulties, and upcoming developments in this crucial field.
1. The Importance of ADAS Testing and Validation
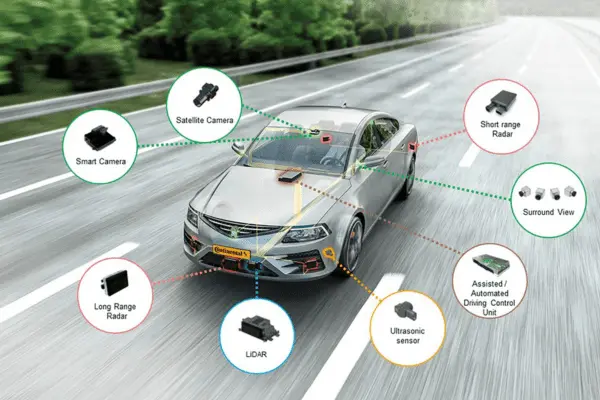
To perform essential functions such as automated emergency braking, adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assistance, and blind spot monitoring, ADAS integrates advanced algorithms, sensors, and actuators. Therefore, to guarantee the correct deployment of these features, thorough testing and validation are required. Furthermore, thorough validation aids in the efficient handling of possible risks and difficulties. Consequently, the system can function seamlessly in practical scenarios, improving both security and efficiency.
The main objectives of ADAS Testing and Validation
- Safety Assurance: Ensuring precise and secure operation in a variety of situations is the main goal of ADAS testing. This lessens the possibility of mishaps brought on by faulty systems or misunderstandings.
- Performance Evaluation: Testing guarantees that ADAS features function dependably in a range of driving scenarios, including on highways, in metropolitan areas, and inclement weather.
- Regulatory Compliance: ADAS systems must adhere to stringent safety standards set by regulatory bodies. Validation is a crucial stage in obtaining legal certification.
- User Experience: To give drivers a seamless, simple, and stress-free experience, it is essential to assess the usability and human-machine interaction.
2. ADAS Testing Types
ADAS testing uses a variety of approaches to guarantee thorough system validation. Specifically, these methods cover every facet of reliability and functionality, from simulations to real-world assessments. As a result, manufacturers can identify and address potential issues before they are implemented, ensuring safer and more efficient systems.
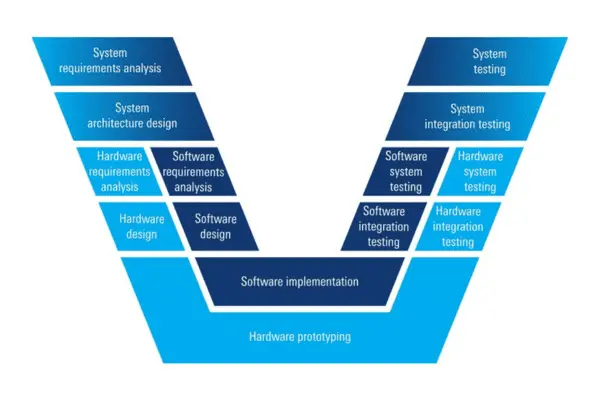
a. Hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) testing
Connecting real ADAS gear, like sensors and Electronic Control Units (ECUs), to a computerized driving simulation environment is known as HIL testing. This makes it possible to evaluate ADAS algorithms in a controlled and repeatable manner without endangering actual assets. The benefits of HIL testing include:
- Sensor integration testing
- assessing the reactions of actuators
- Modeling extreme situations and edge circumstances
b. Testing for Software-in-the-Loop (SIL)
SIL testing evaluates ADAS software algorithms in a virtual environment without utilizing real hardware. With this method, developers can:
- To detect any problems early in the development process, first validate early-stage software.
- Additionally, effectively debug issues without having actual prototypes.
- Lastly, optimize algorithms to ensure a more efficient development cycle by saving time and resources.
c. Testing of Vehicles
- Testing on actual vehicles is necessary to assess ADAS functionality in real-world driving situations. Among the examples are:
- Testing of public roads (with the required safety procedures)
- controlled testing to recreate particular circumstances on proving grounds
d. Testing via Simulation
Evaluation of ADAS systems in a variety of virtual scenarios, such as uncommon or dangerous occurrences that are difficult to recreate in real-world settings, is made possible by simulation testing. Advantages consist of:
- Efficiency in terms of cost
- Adaptability while creating scenarios
- Shorter testing duration
e. Testing Based on Data
One of the main components of ADAS systems is sensor data. Data-driven testing includes examining recorded data from real driving to:
- Verify the ADAS algorithms.
- Boost the resilience of the system
- Make decision-making procedures better
3. Issues with ADAS Validation
Notwithstanding its many benefits, ADAS system testing and validation present several difficulties:
a. Edge Cases
Extreme and unusual circumstances that are uncommon in everyday driving must be taken into consideration during testing. To guarantee system stability and robustness, certain edge cases are essential.
b. Adjusting the Sensor
Accurate sensor calibration is essential for reliable data collection. Otherwise, inadequate calibration may jeopardize the accuracy of the system. For example, it could result in false positives or negatives, endangering both safety and performance. Thus, to guarantee optimal operation, routine calibration and validation are necessary.
c. Compatibility
Modern cars usually include a large number of ADAS components from different providers. It can be difficult to ensure smooth communication between these parts, though. Thus, seamless interoperability and thorough testing are necessary to avoid conflicts and problems.
d. Human Element
Validation processes must take human characteristics into account to ensure safety and boost user acceptability. Designing intuitive systems also requires a grasp of how drivers behave and interact with ADAS elements. Therefore, adding human-centered validation can improve system effectiveness and usability.
e. Constant Updates
For ADAS systems to adapt to evolving driving conditions and difficulties, frequent upgrades are required. Furthermore, these systems need to be continuously improved as traffic scenarios and road conditions change. Therefore, continual validation and improvement are necessary to maintain optimal performance and safety.
4. ADAS Testing and Validation Standards
ADAS validation is governed by several international standards and laws, which guarantee that systems meet safety and performance requirements. Additionally, these rules aid in maintaining uniformity among various markets. Manufacturers are therefore required to adhere to several regulations to guarantee that their ADAS systems fulfill global safety requirements.
a. ISO 26262
This standard covers all phases of development and offers functional safety recommendations for automotive systems, including ADAS.
b. Euro NCAP
Vehicle safety is evaluated, and ADAS technology performance is tested by the European New Car Assessment Program (Euro NCAP). Additionally, it offers safety ratings to assist customers in making wise choices. Therefore, authorities urge automakers to improve their ADAS systems to receive higher safety ratings.
c. Guidelines from the NHTSA
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) offers standards for ADAS validation and testing to ensure compliance with US safety regulations. Additionally, these rules aid in industry-wide standardization of safety procedures. Manufacturers are thus able to create and verify ADAS systems that satisfy legal specifications while guaranteeing the functionality and safety of automobiles.
d. SAE J3016
Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (complete automation) are the levels of driving automation defined by this standard, which also classifies ADAS.
5. Upcoming Developments in ADAS Testing and Validation
Alongside the advancement of ADAS technology, testing and validation methods are changing as well. We are therefore creating new strategies to guarantee precision and reliability. Among the most important upcoming trends are:
a. Testing for artificial intelligence (AI)
Experts will require advanced testing techniques, such as adversarial testing and AI-driven simulations, to integrate AI into ADAS systems and assess decision-making processes.
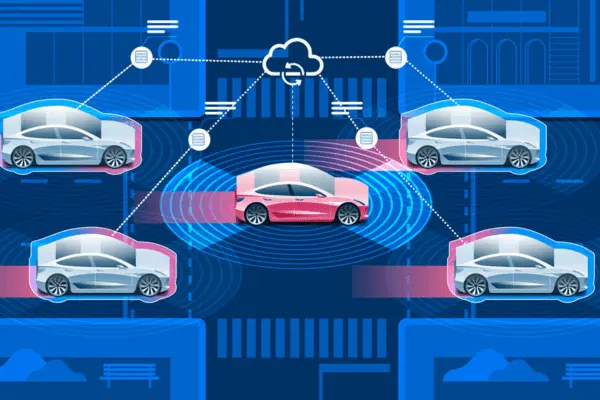
b. Collecting Information in the Real World
- Automakers and developers will give more importance to real-world driving data collection to:
- Improve the functionality of ADAS
- Verify systems under a variety of situations.
c. Testing for cyber security
As connection grows, cyber security testing will become a crucial component of ADAS testing and validation to safeguard systems against cyberattacks. Additionally, the risk of cyber threats will increase as vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication becomes more integrated. Thus, putting strict security measures in place will be essential to guaranteeing the dependability and safety of ADAS systems.
d. Updates via Over-the-Air (OTA)
OTA updates will guarantee that ADAS systems remain up-to-date and operational by facilitating real-time validation and continuous improvements. Additionally, these updates enhance system efficiency and fix software vulnerabilities. Thus, vehicles can maintain high levels of efficiency and safety without requiring in-person service.
Conclusion
Vehicle automation and safety have greatly improved thanks to ADAS technology. However, thorough ADAS testing and validation are necessary to fully fulfill these systems’ potential. Vehicle testing, simulations, data-driven approaches, HIL testing, and SIL testing are all tools that automakers may use to find and fix possible problems and create safer roads and better driving experiences.
Exciting advancements in ADAS testing and validation are anticipated as technology advances. These developments, which range from AI-powered simulations to real-world data integration and OTA updates, will strengthen the position of ADAS in contemporary automobiles.
Contact us at info@dorleco.com to discover more about our outstanding VCU products, CAN Displays, CAN Keypads, and E/E Software services or to find out more about our ADAS testing, validation, and software development experience, especially for battery-specific applications.


