Introduction
Reliability, accuracy, and smooth communication are critical in the dynamic field of industrial automation. Created for automotive purposes, the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus has become a vital industrial communication standard. Its versatility and strong features have made it essential for a wide range of applications, including process control, robotics, and manufacturing.
This blog explores the basic ideas, benefits, uses, and drawbacks of the CAN Bus in industrial automation, emphasizing how revolutionary it is for contemporary industry.
Industrial Automation’s Communication Foundation
A key component of industrial automation is the requirement for effective communication between human-machine interfaces (HMIs), sensors, actuators, and controllers. The backbone of this communication network is the CAN bus, which allows complicated systems to exchange commands and data in real-time.
Created to satisfy the demanding requirements of automotive systems, the CAN bus has demonstrated its value in settings that frequently experience extreme conditions, noise, and electromagnetic interference.
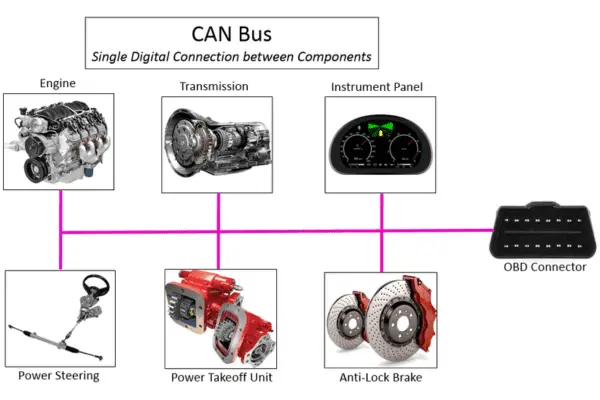
Key Features of the CAN Bus in Industrial Automation
Strong and Dependable Communication: Issues including temperature fluctuations, vibrations from machinery, and electromagnetic interference are common in industrial settings. Even under such unfavorable circumstances, proper data transfer is guaranteed by the CAN bus’s strong signaling mechanisms and error-checking algorithms.
Real-Time Data Transmission: Industrial automation is characterized by time-sensitive procedures.
The CAN bus’s low latency and precise synchronization make it ideal for real-time data in robotics, manufacturing, and process control
The CAN bus scales to add devices without redesigning the system, making it ideal for complex industries like aerospace and automotive.
Benefits of CAN Bus in Industrial Automation
The CAN bus’s distinct advantages have revolutionized industrial automation communication standards:
- Optimal Bandwidth Utilization: The CAN bus prioritizes urgent communications and reduces congestion by only transmitting data when necessary, in contrast to traditional communication systems. This economical use of bandwidth guarantees seamless operation in multi-device networks.
- Standardized Communication: Hardware components from different manufacturers can work together more easily because of the CAN bus’s established protocols. Maintenance and system integration are made easier by this compatibility.
- Decreased Maintenance Costs: Because CAN bus networks are inherently reliable, they require less maintenance and troubleshooting, which lowers operational downtime and saves money.
- Energy Efficiency: In industrial systems, power consumption is a crucial factor. For networked devices, the CAN bus facilitates low-power states, guaranteeing energy efficiency when the device is not in use.
- Fault tolerance: System failures can result in expensive downtime in industrial settings. Because of the CAN bus’s fault tolerance, the network can keep running even if one of its components fails. This resilience lowers operational disturbances and improves system reliability.
- Data Accuracy and Integrity: The CAN bus’s built-in error-checking features guarantee excellent data integrity. For applications where exact data transfer is essential and cannot be compromised, this functionality is essential.
CAN Bus in Industrial Automation Applications
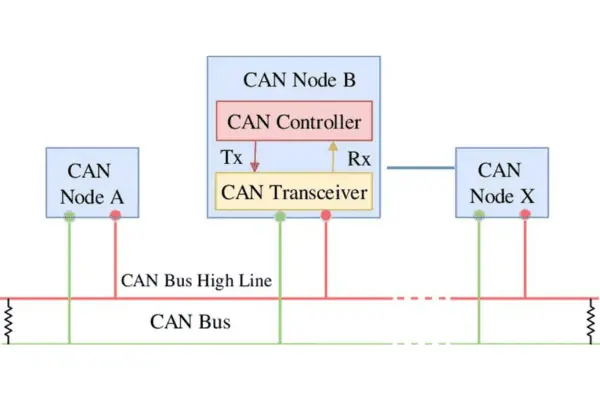
Due to its adaptability, the CAN bus is an ideal option for a wide range of industrial applications.
- Manufacturing Systems: The CAN bus facilitates smooth communication between machines, sensors, and controllers in automated manufacturing. By ensuring synchronized processes, production errors and downtime are minimized.
- Robotics: For accurate control, robotics mostly depends on real-time communication. To improve operational efficiency, the CAN bus facilitates the complex coordination of robotic arms, sensors, and actuators
- Process Control: The CAN bus’s dependable data transport is essential for industries like energy production and chemical processing, as it enables precise monitoring and control of vital operations.
- Vehicle Control Systems: Forklifts and cranes are examples of industrial vehicles that rely on the CAN bus to provide real-time monitoring and control of critical parameters.
- Aircraft and Defence: The CAN bus facilitates the integration of intricate systems in aircraft applications, guaranteeing reliable communication even in the most adverse circumstances.
- Process Control: The CAN bus’s dependable data transport helps industries like energy production and chemical processing by facilitating precise monitoring and control of vital operations.
- Vehicle Control Systems: Forklifts and cranes are examples of industrial vehicles that rely on the CAN bus to provide real-time monitoring and control of critical parameters.
- Aircraft and Defense: The CAN bus facilitates the integration of intricate systems in aircraft applications, guaranteeing reliable communication even in the most adverse circumstances.
- Restricted Timing Determinism: Although the CAN bus facilitates real-time communication, it might not have the deterministic timing that more recent industrial networking solutions provide. For applications needing an exact time, this could be a disadvantage.
- Complicated Configuration and Troubleshooting: CAN bus network configuration can be challenging, especially for large-scale systems. It frequently takes certain equipment and knowledge to diagnose and resolve problems.
- Absence of Built-in Security: When developers created the CAN bus, they did not give top priority to security. Cybersecurity risks in contemporary industrial networks make extra precautions to safeguard CAN bus systems necessary.
Benefits and Drawbacks
Despite its drawbacks, the CAN bus remains crucial in industrial automation for its reliability, scalability, and affordability. Engineers must assess application needs while weighing its pros and cons.
As emerging technologies continue to evolve, they have the potential to address some of the CAN bus’s drawbacks. Consequently, these advancements may enhance its efficiency and adaptability, thereby ensuring its continued relevance in industrial settings. Cybersecurity innovations and integration with more recent communication protocols can further increase its capabilities.
Conclusion
Because it offers a dependable, scalable, and effective communication structure, the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus has revolutionized industrial automation. Its real-time data handling, error resistance, and system integration make it vital in robotics and aviation.
The CAN bus does have some limits, though, much like any other technology. Its adoption requires planning and extra security due to limited bandwidth, distance limits, and no built-in security.
The function of the CAN bus in industrial automation technology advances. Its versatility ensures it remains vital for connecting machines in complex industrial settings.
Dorleco provides innovative solutions for companies looking for premium VCU products, CAN Keypads, CAN Displays, and software services designed for battery-specific applications. To find out how we can improve your industrial automation systems, send us an email at info@dorleco.com.