Introduction to CAN Bus Vs RS485
In industrial and automation applications, communication protocols are essential because they allow for smooth device interaction and effective data sharing. Two popular protocols in this area are the Controller Area Network (CAN) and Recommended Standard 485 (RS485). Each is appropriate for particular use instances due to its distinct features, benefits, and limitations. To help you choose the best protocol for your application, we will examine the distinctions between these protocols, as well as their advantages, disadvantages, and important uses in this post, CAN Bus Vs RS485.
What is the CAN Protocol?
To handle the growing complexity of communication within automobiles, Robert Bosch GmbH developed the CAN protocol in the 1980s specifically for automotive applications. Its qualities—like fault tolerance, real-time communication, and high reliability—have over time made it a popular option in a variety of other areas, such as industrial automation, medical devices, and aerospace.
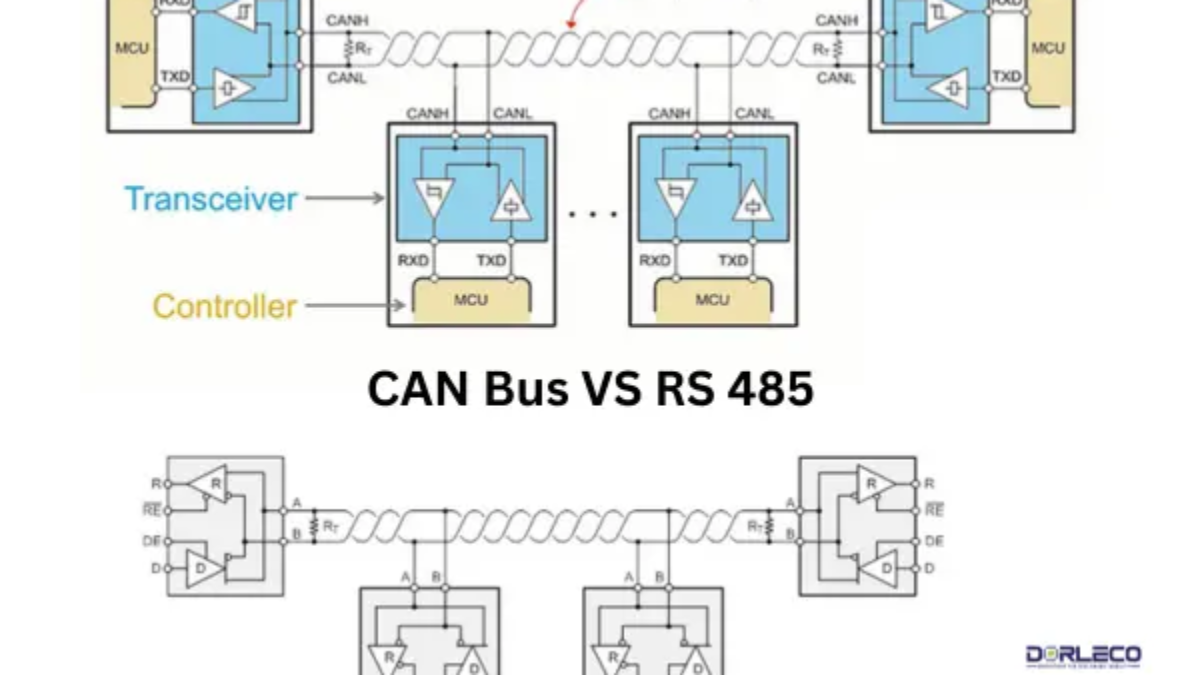
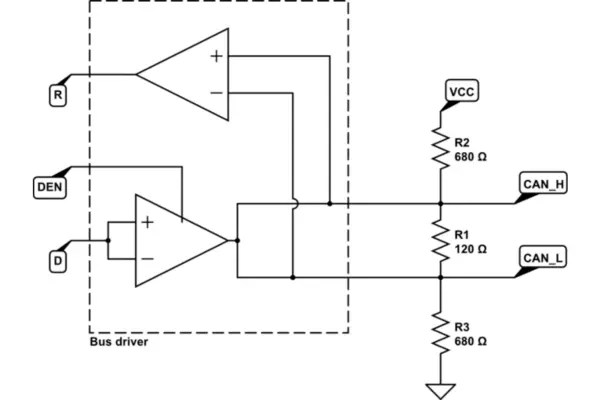
Important CAN Protocol Features:
- Bus-Based Communication: The CAN protocol operates on a two-wire bus, utilizing a CAN High (CANH) line and a CAN Low (CANL) line to facilitate communication.
- Message-Based Communication: Receiving devices can identify and prioritize messages since each one has a unique identity.
- Collision detection and arbitration: This minimizes collisions and maximizes efficiency by guaranteeing that only one device transmits data at a time.
- Operating Temperature: CAN endure temperatures ranging from -40°C to +85°C, allowing it to operate in harsh conditions.
Benefits of the CAN Bus:
- High speed and Bandwidth: CAN is perfect for real-time communication in applications like robotics and engine management since it can transport data at up to 1 Mbps.
- Multi-Master/Multi-Slave Communication: This facilitates effective device-to-device communication by allowing several devices to send and receive data over a single communication channel.
- Fault Tolerance: Even in noisy situations, CAN’s strong error detection and repair methods guarantee dependable communication.
- Scalability: The CAN bus provides flexibility for future growth by being easily scaled to suit different system sizes.
- Robustness: The CAN bus can endure both electrical and physical stress because it was built for severe situations.
Limitations of the CAN Bus
1. Greater complexity and cost:
Compared to simpler protocols, the sophisticated features and greater data rates increase the complexity and cost of implementation.
2. Restricted Range:
Applications needing long-distance communication may find CAN unsuitable because it is normally only 40 meters at high speeds and 500 meters at reduced speeds.
3. No power supply:
Because the protocol does not provide a power supply, devices on the CAN bus must rely on their power sources.
4. Applications of the CAN Bus
- Automotive: The CAN Bus is widely used in automotive applications, including electronic control units, in-car communication systems, and engine diagnostics.
- Aerospace: guidance, navigation, and control avionics systems.
Industrial automation is the process of sensors, actuators, and controls communicating in real-time. - Medical Devices: Monitoring systems, infusion pumps, and ventilators that communicate.
- Railways: Signaling, traction, and brake control systems.
What is RS485?
RS485 is a point-to-point communication protocol specifically designed for automation and industrial systems that require data transmission over vast distances. RS485 is a popular protocol for linking sensors, actuators, and controllers because of its ease of use, durability, and noise immunity.
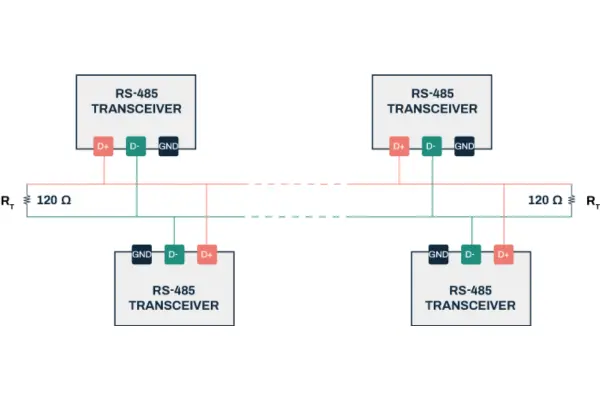
Key characteristics of the RS485
Differential signals include their excellent noise immunity and low interference due to the usage of two wires with opposing voltages for data transmission.
RS485 uses a master-slave paradigm in which a single device connects with several slaves while acting as the master.
When it comes to long-distance communication, it is specifically designed to transmit information over distances of up to 1200 meters.
Benefits of RS485
- Long-Distance Communication: RS485 is perfect for applications like building automation or industrial facilities where devices are dispersed across wide areas.
- Multi-Point Communication: Multiple devices can effectively share a single communication line thanks to the protocol’s provision for multi-point connections.
- Noise Immunity: Even in noisy settings, dependable communication is ensured by the differential signaling technique, which reduces the effects of electrical noise.
- Low Cost: RS485 is a cost-effective solution because it only needs cheap parts and basic wiring.
- Implementation Ease: RS485 requires no sophisticated hardware or software and is easy to use for simple automation requirements.
Limitations of RS485
1. Reduced Data Rate:
Compared to more recent protocols, RS485 has a lower data rate (up to 10 Mbps), which restricts its applicability for high-speed applications.
2. Restricted Bandwidth:
The quantity of data that can be sent concurrently is limited by the protocol’s bandwidth restrictions.
3. Half-Duplex Communication:
4. No Power Delivery:
Similarly, RS485 devices require their power sources, just like CAN.
Applications of RS485
- Industrial Automation Applications: Linking sensors, actuators, and controls in manufacturing facilities.
- Building Automation: This includes managing air conditioning, lighting, and other infrastructure.
- Security Systems: Communication between access control, alarms, and cameras is made possible by security systems.
- Transportation: Applied to equipment monitoring, ticketing machines, and passenger information displays.
- Energy Management: Energy management is keeping an eye on and managing a facility’s energy use.
Comparison: CAN Bus Vs RS485
| Feature | CAN Bus | RS485 |
| Communication Method | Bus-Based | Point-to-Point |
| Speed and Bandwidth | Speed Rapidity (up to 1 Mbps) Speed | Moderate (up to 10 Mbps) |
| Distance and Topology | Up to 500 m; Bus Topology | Up to 1200 m; Daisy Chain Topology |
| Fault Tolerance | High | Moderate |
| Cost and Complexity | Higher | Lower |
| Applications | Automotive, Aerospace, Robotics | Industrial Automation, Building Automation |
Performance and Physical Features of CAN Bus Vs RS485
1. Physical Layer:
- CAN signals by using a voltage differential between CANH and CANL.
- RS485 uses two lines with balanced signals and a voltage differential.
2. Maximum Length of Cable:
- While RS485 can reach up to 1200 meters, CAN only reach up to 500 meters.
3. Rate of Data Transfer:
- While CAN only provides 1 Mbps, RS485 can reach up to 10 Mbps.
4. Error Handling:
- Integrators implement error detection and repair systems via CAN.
- For error handling, RS485 depends on additional hardware and software.
Conclusion
The particular needs of your application will determine whether to use RS485 or CAN Bus.
Select CAN Bus for:
- fast, instantaneous communication.
- applications that require scalability and strong fault tolerance.
- Use in automotive, aerospace, or distributed control systems.
Select RS485 for:
Additionally, it enables economical and long-distance communication.
simpler, more durable applications, such as energy management or building automation.
By thoroughly understanding the distinct features of each protocol, engineers can therefore make well-informed decisions. As a result, they can ensure optimal performance and reliability in their systems
Both RS485 and CAN Bus have shown their value across a range of industries, and as technology advances, so does their usefulness.
Our specialty at Dorleco is providing state-of-the-art VCUs, CAN displays, and CAN keypads. E/E Software Services are designed to take advantage of the sophisticated features of the CAN Bus for dependable, real-time communication in industrial automation, automotive, and aerospace applications. For more intelligent networking solutions, collaborate with Dorleco.