Introduction
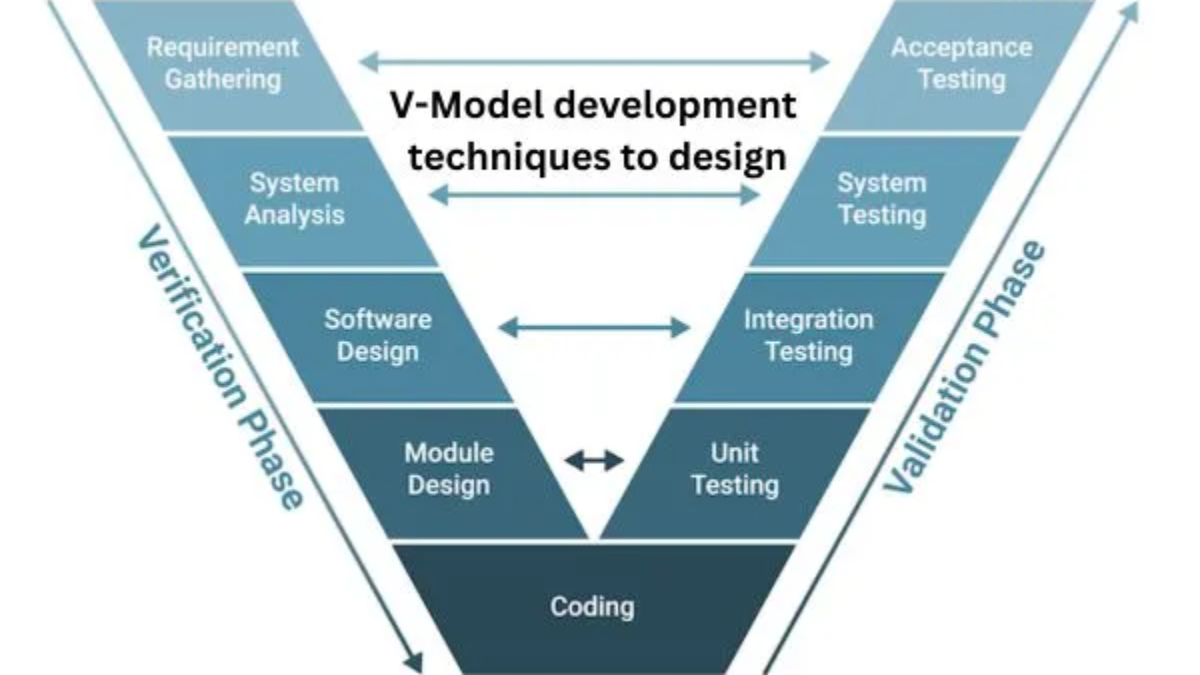
The Verification and Validation Model, often known as the V-Model or the V-Cycle, is a software development methodology that prioritizes testing throughout the entire process. It’s a waterfall approach modification that’s widely used in critical system development when thorough testing is necessary. The V-Model’s two main stages are completed in the following order:
1. Verification (left side of the V):
a. Analysis of requirements:
– Identify and document the client’s needs.
– Based on customer input, determine software and system requirements.
b. System Design:
Develop a high-level design specification by referring to the requirements.
– Explain the system’s overall architecture.
c. Architecture:
Create a comprehensive system architecture.
– Explain the interfaces that the system’s various components have with one another.
d. Module Design:
Break the system up into smaller, easier-to-manage parts.
– Clearly define each module’s requirements.
e. Implementation (Coding):
Write code according to the detailed module requirements.

1. Examining units:
– Check that each module is accurate.
– Identify and fix module-level issues.
2. Validation (right side of the V):
a. Testing for integration:
To ensure that the modules work as a whole, integrate them and test them all together.
– Find and correct any errors in the modules’ interlobular communication.
b. Testing the system:
Test the system as a whole to make sure it meets the requirements.
Identify and fix issues at the system level.
c. The user acceptance test, or UAT:
– Validate the solution by asking end users to attest that it meets their needs.
– Get user input and make necessary adjustments.
d. Initiation:
After testing is completed successfully, put the system into use.
Make sure that the necessary documentation has been completed.
1. Upkeep and Assistance:
Assist continuously, fix issues that arise in the real-world setting, and implement any necessary improvements.
Important ideas and methods related to the V-Model:
The V-Model encompasses several fundamental concepts and techniques that guide its application in software development. The main concepts and techniques associated with the V-Model are as follows:
Initial Testing
Principle: Testing activities are initiated early in the development life cycle.
Technique: Unit testing is used in the early stages of test preparation and execution to guarantee that errors are identified and corrected as soon as practical.
2. An incremental and phased approach:
Principle: Development and testing have distinct periods.
Methodology: Testing is organized based on the stages that make up the development process. Additionally, incremental development allows systems that are only partially functional to be sent for testing and validation. As a result, issues can be identified and addressed early, leading to a more efficient and reliable final product.
3. Trackability:
Principle: To ensure consistency and validation, there should be a clear, traceable relationship between requirements and relevant tests. Moreover, this alignment helps verify that all requirements are properly addressed. As a result, potential gaps can be identified and resolved early in the development process.
Method: Make and maintain traceability matrices that link each requirement to the tests that verify its fulfillment. This ensures that all tests are covered thoroughly.
4. Loops of Feedback:
Principle: Continuous input is essential during the development and testing phases.
Methodology: As defects are found during testing, they are communicated to the development team for resolution. The quality of the software is improved by this loop of iterative feedback.
5. Record-keeping:
Concept: To ensure clarity and consistency, every stage of development and testing requires extensive documentation. Moreover, proper documentation helps track progress, identify issues, and maintain alignment with project goals. As a result, teams can work more efficiently while ensuring high-quality outcomes.
The method entails producing and maintaining current, comprehensive documentation for the design, requirements, test cases, and test plans. Furthermore, this documentation serves as a guide and comprehension tool throughout the system’s lifecycle. As a result, it ensures consistency, enhances collaboration, and supports effective decision-making.
6. Testing and Development in Parallel:
Concurrent development and testing is the idea that both operations happen at the same time.
Methodology: Testing for each phase is ongoing as the related development stage moves forward. Using a parallel approach reduces the likelihood that teams will identify and solve major defects sooner, preventing them from emerging later.
7. Well-defined positions and responsibilities:
It is important to specify the roles and duties of the development and testing teams to ensure smooth collaboration and efficiency. Additionally, well-defined responsibilities help prevent confusion and enhance accountability. As a result, projects can be completed more effectively while maintaining high-quality standards.
Method: Assign specific duties to individuals or teams for each level of the V-Model to establish accountability and clarify who is in control of what. Furthermore, this structured approach ensures that we clearly define responsibilities, which in turn reduces confusion and improves efficiency. As a result, teams can collaborate more effectively and maintain a streamlined workflow. As a result, the development and testing processes become more organized and effective.
8. User Engagement:
Principle: User engagement is necessary for both validation and acceptance.
Method: To ensure the system meets users’ needs and expectations, it is important to involve them in the User Acceptance Testing (UAT) stage. Moreover, their input provides valuable insights that help refine the system. Consequently, this leads to a more user-friendly and efficient final product.

9. Management of Configurations:
Principle: It is important to supervise and carefully control any changes made to the software and its associated resources to ensure stability and consistency. Moreover, maintaining proper oversight helps prevent unintended disruptions and ensures that we implement updates smoothly.
Technique: To maintain version control, monitor changes, and ensure consistency between development and testing, it is therefore essential to implement configuration management procedures.
10. Comprehensive Testing:
Principle: To ensure reliability, we ought to thoroughly test all aspects of the system. Furthermore, comprehensive testing helps identify potential issues before deployment. As a result, the system can operate smoothly and efficiently, minimizing the risk of failures.
Technique: Plan and execute a range of tests, including unit, integration, system, and user acceptance testing, to confirm the program’s accuracy and dependability.
Drawbacks of the main ideas and methods connected to the V-Model
Even though the V-Model offers a structured approach to software development with integrated testing, it is not without its drawbacks. The following are some limitations and drawbacks associated with the primary concepts and techniques of the V-Model:
1. Inflexibility and rigidity:
Cons: When it comes to modifying needs, the V-Model could be less adaptable and more rigid. It makes the challenging assumption that needs are clear and unchanging, which makes it challenging to adjust as the project develops.
2. System Visibility After Hours:
Cons: It takes a long time for the system to become fully visible during the development life cycle. This could lead to erroneous perceptions of user requirements or a delay in identifying design flaws, which makes problem-solving more challenging and costly.
3. Minimal User Engagement:
4. Dependency on Proactive Scheduling
Limitation: The effectiveness of the V-Model depends on having a firm understanding of the needs and starting early. If the needs change or the initial planning is flawed, delays and significant barriers could occur.
5. Nature in Sequence:
Cons: The V-Model follows a sequential path in which the completion of one phase depends on the success of the one before it. This could lead to a longer development timeframe, especially if the team requires changes after the project starts.
6. Insufficient Length for Iterative Development:
Cons: Iterative or incremental development approaches do not work well with the V-Model. Moreover, it may not be compatible with modern agile methodologies, which strongly emphasize flexibility and quick adaptation to changing requirements.
7. Excessive Focus on Testing
Cons: The V-Model may overemphasize testing as a stand-alone step, even though testing is crucial. This approach could not be effective for projects incorporating agile methodologies, which call for continuous testing and feedback
8. Presumption of Clearly Stated Needs:
Cons: The V-Model is based on the assumption that needs are precise and unchanging from the outset. As the team develops the project, they may need to make adjustments because needs often change.

9. Low Level of Client Involvement
Cons: User acceptability testing and requirements phases are usually the only times we communicate with customers or stakeholders. Consequently, this limited interaction can lead to a lack of ongoing contact and feedback throughout the development process.
10. Having difficulties handling difficult projects?
Cons: The V-Model may confront challenges when large, complicated projects do not completely understand their requirements upfront. An iterative and more flexible approach may be more appropriate in some circumstances.
Conclusion:
In summary, the V-Model’s core principles and techniques provide a structured, methodical approach to software development that emphasizes early testing and traceability. However, it’s crucial to consider both the benefits and drawbacks of the V-Model:
When choosing the V-Model, it’s critical to consider the project’s needs for stability, the organization’s overall development plan, and the project’s type. The V-Model suits projects needing a systematic, well-documented process with minimal or well-managed changes. However, for projects that require more flexibility and adaptability, different methodologies like Agile may be more appropriate.