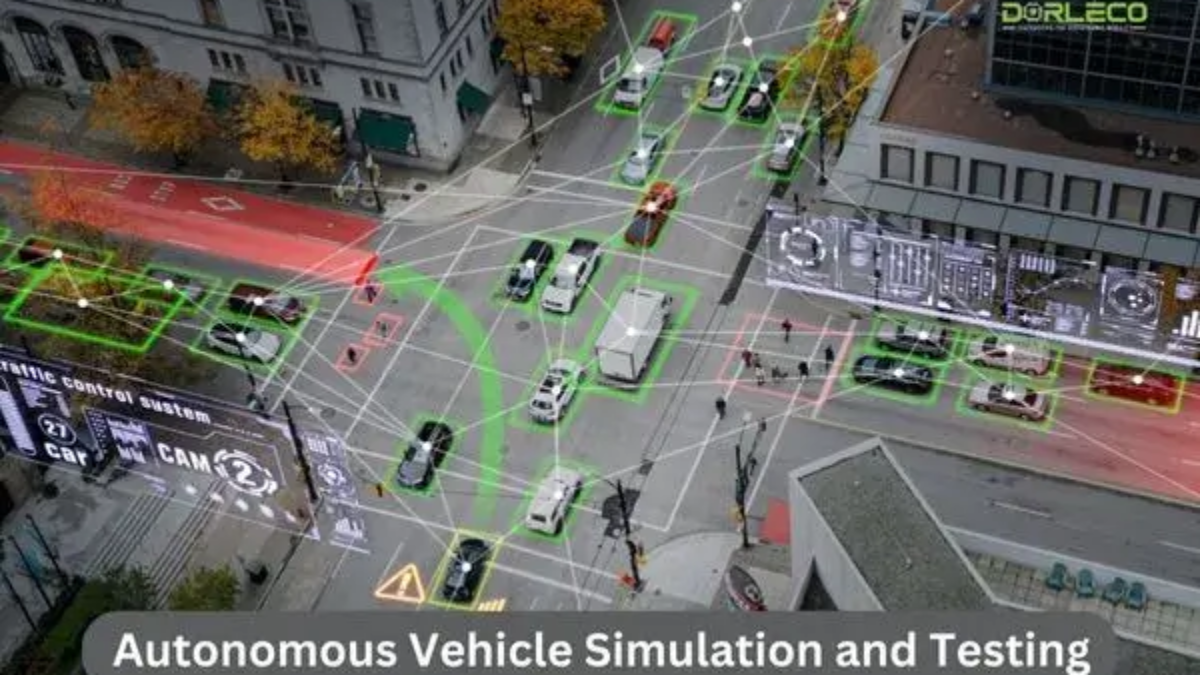
Introduction
In the auto industry, autonomous vehicles—also referred to as self-driving cars—are a game-changer. These vehicles could increase transit’s efficiency, safety, and accessibility. Before being used on a large scale, they must first undergo extensive modeling and testing to ensure their dependability and safety. This introduction highlights the importance, key components, and challenges of autonomous vehicle simulation and testing while providing a broad overview of these processes.
1. The value of Autonomous Vehicle Simulation and Testing
- Safety Assurance: Ensuring the safety of self-driving automobiles is essential. Testing and simulation provide a controlled environment in which possible system faults can be identified and fixed, averting mishaps and maintaining public trust.
- Regulatory Compliance: Tight regulations apply to autonomous vehicles. Manufacturers can use autonomous vehicle simulation and testing to show that they meet these requirements.
- Cost-Efficiency: Testing in actual environments can be expensive and time-consuming. Simulations enable cost-effective testing and rapid data collection.
- Performance Optimization: Through autonomous vehicle simulation and testing, autonomous vehicle systems can be tuned for optimal responsiveness, dependability, and performance.
2. Components of Autonomous Vehicle Testing and Simulation:
- Sensor Simulation: LiDAR, radar, cameras, GPS, and other sensors are some of the many sensors that autonomous cars use. Simulations that mimic sensor inputs assess how the vehicle reacts to different circumstances.
- Environment modeling: Virtual environments are created to replicate real-world events, including traffic, pedestrians, and weather. This enables testing under numerous challenging conditions.
- Behavioral Modelling: To evaluate a vehicle’s ability for safe navigation, simulation models its behavior, including course planning and collision avoidance.
- Data Logging and Analysis: A lot of data is gathered during tests and simulations, and this data is analyzed to identify any issues, validate system functionality, and improve algorithms.
3. Types of Testing:
- Hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) testing involves evaluating the autonomous vehicle’s hardware in a simulated environment, including its controllers and sensors. Consequently, it is possible to perform early validation without deploying the full vehicle.

- Software-in-the-loop (SIL) testing: This type of testing involves running an autonomous vehicle’s software in a simulated environment. It assesses the vehicle’s decision-making procedures and algorithms.
- Vehicle-in-the-loop (VIL): Using real cars, technology simulates traffic and surroundings. This tactic establishes a connection between simulation and real-world testing.
- Real-World Testing: On closed tracks and open highways, real-world testing is done to confirm system performance when autonomous vehicle simulation and testing in safe situations are successful.
4. Difficulties:
- Realism: Achieving a high degree of realism in simulations can be challenging. Realistic climatic conditions must be accurately reflected in simulation settings.
- Diversity of Scenarios: It is imperative to test autonomous vehicles in a range of scenarios, including unusual and edge cases that can be difficult to fully recreate.
- Regulatory Structure: Developing a clear legislative framework for autonomous vehicle testing and certification is a challenging and ever-changing process.
- Cybersecurity: Security testing is a crucial phase in the development process because autonomous vehicles are vulnerable to hackers.
Benefits of Autonomous Vehicle Simulation and Testing
Autonomous vehicle simulation and testing provide many benefits that make it possible to build and use self-driving cars. The following are some of the main benefits:
1. Improvement of Safety:
Autonomous vehicle simulation and testing provide a secure and regulated environment for identifying and resolving possible security issues. This lowers the dangers associated with autonomous cars.
2. Lower Testing Expenses in the Real World:
Simulation testing is more cost-effective when compared to testing on real roads. When expenses for fuel, upkeep, and actual test tracks are removed, development becomes more efficient and less expensive.
3. Capability to Scale:
Through simulations, engineers may evaluate an autonomous vehicle’s performance in a range of conditions, facilitating rapid scaling and obviating the need for extensive real-world testing.
4. Repeatability of Scenarios:
Because they accurately replicate conditions and scenarios, simulated environments facilitate the comparison of results, validation of changes, and prediction of vehicle behavior in a variety of scenarios.
5. Fast Iteration
Simulation enables engineers to identify issues early on and take action to address them, leading to faster development of hardware and software.

6. Information Gathering and Evaluation:
Massive amounts of data from simulated testing are produced, enabling in-depth analysis and better understanding as well as performance adjustment of the self-driving car.
7. Security and Privacy:
By preventing critical data or proprietary technologies from being exposed on public roadways, simulated testing reduces the risk of intellectual property theft and privacy concerns.
8. Flexibility:
Simulations can mimic a range of driving conditions, including extreme ones that are dangerous or challenging to duplicate in real-world testing, to perform an exhaustive analysis.
Drawbacks of Testing and Simulating Autonomous Vehicles
While there are numerous advantages to
autonomous vehicle simulation and testing, these techniques also come with certain challenges. Some disadvantages of testing and modeling driverless vehicles are as follows:
1. Strict Realism
The intricacy of real environmental conditions may not always be correctly reflected in simulated environments, which could cause issues when assessing the performance of autonomous vehicles. Unrepresentative elements can include alterations in infrastructure, unmodeled road dangers, and unexpected behavior.
2. Excessive Fitting:
If developers have predominantly optimized autonomous systems using simulation data, these systems may perform poorly when faced with unexpected real-world environments.
3. Realism of Sensors:
Simulated sensor data may not fully reflect the subtleties of actual sensor inputs. As a result, this could lead to discrepancies in the system’s performance between simulation and real-world scenarios involving human drivers. Therefore, it is crucial to refine sensor modeling techniques to enhance the reliability and accuracy of autonomous vehicle simulations.
4. Partial Coverage of Scenarios:
For simulations, creating an extensive scenario library can be a challenging and time-consuming task. It’s possible to overlook peculiar but significant events that are crucial to determining an autonomous vehicle’s level of safety.
5. Uncertainty in Simulations:
The modeling of the simulation environment may contain errors and uncertainties that compromise the validity of test results. Consequently, inadequate simulation testing could create a false sense of security, potentially leading to unforeseen risks in real-world deployment. Therefore, it is essential to ensure rigorous validation and continuous improvement of simulation models.
6. Complexity of Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL):
Because
HIL simulations combine real hardware with virtual environments, they can be costly and challenging to set up and maintain. It could be challenging to synchronize and calibrate hardware components.
7. Needs for Data and Processing:
During simulation, researchers generate enormous amounts of data, and they must process, store, and analyze these quantities of data, which can be expensive and resource-intensive.

8. Dynamic Interactions with Traffic:
Mimicking real-time interactions with other road users, including cyclists, pedestrians, and human drivers, can be challenging. This is primarily due to their unpredictable nature and the need for high-fidelity modeling. Therefore, developing accurate and responsive simulation systems is crucial for improving autonomous vehicle performance in real-world scenarios.
Conclusion:
To sum up, autonomous vehicle simulation and testing are essential steps in the creation and application of self-driving automobiles. These procedures are essential for improving the usefulness, safety, and dependability of autonomous systems. Although these approaches have advantages and disadvantages, taken as a whole, they positively impact and will significantly influence how we develop transportation in the future.
However, it’s crucial to recognize the difficulties and constraints associated with autonomous vehicle testing and simulation, like the requirement for accurate modeling, the possibility of overfitting, and the complexity of edge cases. Testing in the real world is still necessary to verify the technology in complicated and unpredictable environments.
Real-world testing and simulation must coexist for autonomous cars to meet the required safety and dependability requirements. Consequently, the continuous development and integration of these techniques will play a crucial role in shaping the future of transportation. Moreover, this advancement will pave the way for safer, more efficient, and more accessible autonomous vehicle simulation and testing.
Stay informed about our latest
VCU products and
autonomous vehicle simulation and testing services. For more information, contact us at
info@dorleco.com or visit our website at
Dorleco-Home | Dorleco