Introduction
The term “road dynamics” covers a broad spectrum of subjects related to the behavior and interactions of automobiles with their environment. It comprises examining forces, motions, and situations that affect an automobile’s comfort, security, and functionality while being driven. Some crucial components of road dynamics are as follows:1. Road Dynamics:
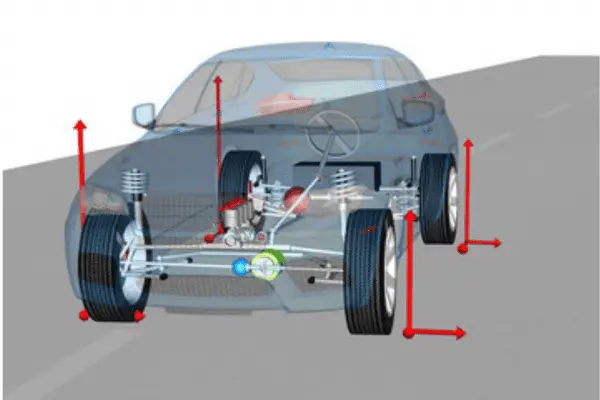
- Suspension Systems: An automobile’s suspension system is necessary to maintain the tires’ contact with the road. It helps to regulate the vehicle’s stability, ride comfort, and handling.
2. Features of tires:
Tire properties like size, tread pattern, and air pressure affect traction, grip, and overall handling on different types of roads.- Braking Systems: The brakes on a car are essential for controlling speed and ensuring safe stops. Effective braking improves the car’s overall dynamics and safety.
- Steering Systems: The steering mechanism of a car affects how it reacts to input from the driver. Proper steering dynamics are required to maintain control during turns and maneuvers.
3. Conditions of the Road Surface:
- Pavement Quality: The condition and caliber of the road surface have an impact on vehicle dynamics. Well-maintained roads provide advantages like improved handling and more comfortable trips.
- Friction and Grip: The way the tires engage with the pavement affects both friction and grip. The road roughness, temperature, and moisture content all affect these interactions.
4. Environmental Components:
- Weather: Unfavorable meteorological conditions, such as snow, ice, or rain, can interfere with the dynamics of roadways. The reduced visibility and sloppy weather can impact an automobile’s performance.
- Effect of Temperature: Extremely high or low temperatures can affect the properties of automotive parts and road surfaces. For instance, hot weather may soften road surfaces, which may decrease tire traction.
5. Traffic Conditions:
- Traffic Flow: The dynamics of a road network are influenced by various factors, such as traffic patterns, congestion, and the activities of other vehicles. Intelligent transportation systems aim to improve traffic flow efficiency and safety.
- Crossings and Intersections: Traffic control and careful planning are necessary due to the unique vehicle dynamics involved in pedestrian crossings and intersection maneuvers.
6. Simulating and Modelling:
- Computer Simulations: With the use of complex computer simulations, engineers and researchers may simulate road dynamics and analyze vehicle behavior under various conditions. This contributes to the development of more efficient and safe road systems.
7. Control Systems for Vehicles:
Electronic control systems, including ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) and ESC (Electronic Stability Control), are commonly found in modern cars to enhance vehicle dynamics and safety.Road Dynamics advantages
Gaining an understanding of and improving vehicle dynamics not only has multiple benefits in various areas of transportation and road infrastructure but also contributes to overall safety, efficiency, and sustainability. Here are a few key advantages:1. Traffic Safety
- Accident Prevention: Potential risks and hazards can be identified by looking at the dynamics of the road. Based on this understanding, safety features can be included to prevent accidents.
- Electronic Stability Control (ESC): Vehicle dynamics have a significant impact on the effectiveness of ESC systems, which can help reduce sliding and boost vehicle stability, especially under challenging driving circumstances.

2. Design and upkeep of infrastructure:
- Pavement Design: Online courses facilitate the design of pavements that minimize road and vehicle wear and tear and increase vehicle comfort.
- Maintenance Planning: Improving overall road condition and safety, maintenance planning enables authorities to promptly address issues such as uneven pavements and potholes by prioritizing repair tasks. A vehicle’s dynamics are assessed to achieve this.
3. Managing Traffic:
- Optimizing Traffic Flow: Road dynamics are a key component of efficient traffic management. This includes scheduling intersection lights optimally, implementing intelligent transportation systems, and controlling lane changes.
- Reducing Congestion: Understanding how traffic interacts with the road environment is necessary to develop strategies to reduce traffic congestion and improve overall traffic flow.
4. Vehicle Performance:
- Enhanced Handling and Stability: Improved Handling and Stability The design of automobiles with improved handling and stability benefits from an understanding of road dynamics.
- Fuel Efficiency: Smoother-running automobiles use less fuel and have a lower environmental impact. This is made possible by improving road dynamics.
5. Transportation Planning:
- Infrastructure Development: Road dynamics inform choices concerning the layout and construction of new roads as well as the expansion of current ones by taking into account factors including topography, traffic patterns, and environmental factors.
- Public Transportation: A knowledge of vehicle dynamics enhances the reliability and efficiency of mass transit systems by helping to design and improve public transportation routes.
6. Impact on the Environment:
- Lower Emissions: Two things that contribute to a decrease in overall vehicle emissions are smoother driving and fewer idling. These variables also include improved vehicle dynamics and smooth traffic flow.
- Green Infrastructure: Two examples of solutions that can be accomplished by fusing an awareness of traffic dynamics with green infrastructure planning are permeable pavements and environmentally friendly landscaping.
7. Emergency Response: Scheduling:
- Route Planning: Emergency responders need to plan their routes with an awareness of road dynamics to guarantee timely and effective assistance during emergencies.
- Evacuation Planning: When developing evacuation plans, factors such as route capacity, traffic patterns, and potential bottlenecks are taken into consideration.
8. Advancements in Technology:
- Autonomous Vehicles: A comprehensive grasp of road dynamics is necessary to properly integrate autonomous vehicles and guarantee that they can handle a range of road conditions.
- Road dynamics play a crucial role in the development of connected vehicle technologies, which, in turn, significantly enhance safety and efficiency by enabling real-time communication between cars and infrastructure.
Road Dynamics Drawbacks
While there are many advantages to knowing and comprehending road dynamics, there are also disadvantages and difficulties. Here are some things to think about:1. Variability and Complexity:
- Dynamic Environment: A few examples of constantly changing dynamic environments are the weather, traffic patterns, and road surface conditions. Because of these complexities, developing general models that reliably forecast vehicle dynamics in every situation is difficult.
- Understanding and being aware of traffic dynamics has numerous benefits, but there are drawbacks and challenges as well. The following are some points to consider:
2. Complexity and Variability:
- Dynamic Environment: A few examples of constantly changing dynamic environments are the weather, traffic patterns, and road surface conditions. It is difficult to develop universal models that precisely predict road dynamics in every situation due to the intricacy of these components.
3. Human Factors:
Human activity, including decisions, responses, and adherence to traffic laws, increases the unpredictability of road dynamics. Differences in driving style and skill can affect the overall efficacy and safety of the road network.- Adaptation Challenges: The introduction of new technologies or road designs based on a better understanding of road dynamics may make it more difficult for users to accept and adapt. It can take some time for cars and pedestrians to become used to the new situation.
4. Price and Execution:
- Infrastructure Upgrades: Major financial investments are often required for modifications to improve the dynamics of the road, such as repainting the pavement or installing advanced traffic control systems. Budgetary restrictions could make it more difficult to carry out necessary changes.
- Adoption of New Technology: Due to budgetary constraints, incorporating state-of-the-art technology such as communication systems and smart sensors into the existing road infrastructure can be costly and challenging.
5. Impact on the Environment:
- Construction and Maintenance: The construction and upkeep of roads may have negative effects on the environment, such as issues with soil erosion, habitat destruction, and water runoff.
- Vehicle Emissions: While better road dynamics may result in more fuel efficiency, concerns remain regarding the overall environmental impact of road transportation, which includes vehicle emissions and the carbon footprint associated with road construction.
6. Privacy and Security Concerns:
- Data Gathering: A common component of sophisticated vehicle dynamics management is the collection and analysis of enormous amounts of data, especially information on vehicle movements. This raises concerns about privacy and the safe handling of sensitive data.
- Cybersecurity Risks: As road infrastructure is more connected and technologically sophisticated, there is a higher likelihood of cybersecurity assaults, which might jeopardize the security and functionality of networks.
7. Unexpected Difficulties:
- Emerging technology: The rapid advancement of new technologies, such as autonomous vehicles, may pose unforeseen challenges and uncertainties to the effective traffic dynamics management process.
- Natural disasters: Events like earthquakes, floods, or other natural disasters can significantly impact road infrastructure, leading to unexpected changes in vehicle dynamics and posing challenges for transportation networks.
Conclusion:
In summary, road dynamics significantly influence the effectiveness, security, and sustainability of transportation networks. Understanding car- road interactions is crucial for infrastructure planning, safety measures, and traffic flow optimization. However, challenges include dynamic complexities, infrastructure limits, human factors, and environmental concerns.A multidisciplinary strategy that integrates engineering, technology, and urban planning improves vehicle dynamics.
Advanced technology improves road safety, traffic management, and vehicle performance through real-time monitoring, intelligent systems, and simulations but faces adoption barriers like cost, infrastructure, and public perception.


