Introduction:
The Transmission Control Unit (TCU) is the centerpiece of the intricate dance between an automobile’s engine and transmission. This hidden hero of automotive engineering has a significant impact on the driving experience and fuel economy since he is critical to enabling smooth and effective shift transitions.
This blog post will go into the world of transmission control units, their functions, and the tactics they employ to makeshift transitions in modern automobiles as smoothly as possible.
The Transmission Control Unit (TCU): An Overview
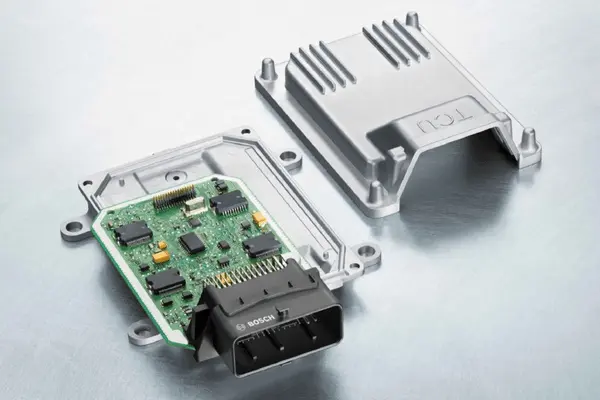

The transmission control unit is a critical component of the car’s powertrain control system. It is a sophisticated electronic control mechanism that monitors the transmission’s functionality. Its primary objective is to govern gear shifts so that the engine always delivers the proper amount of power to the wheels. TCUs accomplish this through the use of sophisticated sensors, algorithms, and feedback loops.
The Function of TCUs in Shift Transitions:
- Determining shift points: TCUs monitor multiple variables, including speed, engine load, throttle position, and road conditions. They use this data to calculate the best time to start a gear shift. This assessment considers factors such as fuel economy, acceleration, and driving comfort.
- Shift Actuation: After detecting that a gear change is required, the Transmission Control Units send instructions to the transmission to perform the shift. As a result, clutches must be engaged and disengaged, gears must be rotated, and hydraulic pressure within the transmission must be adjusted.
- Adaptive Learning: Today’s TCU shift patterns are enhanced over time by utilizing adaptive learning algorithms. To provide a more personalized driving experience, they assess a driver’s behavior and adjust shift points accordingly.
Shift Transition Optimization:
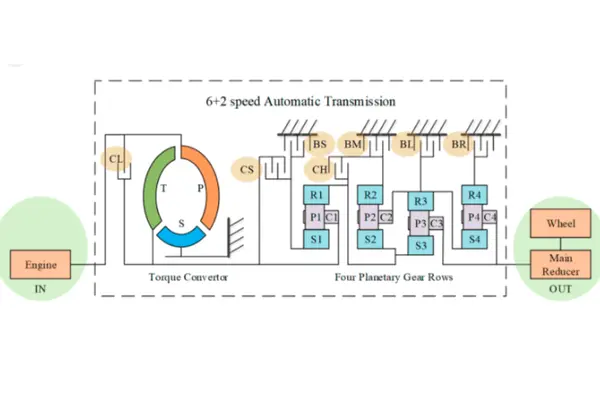
Let’s look at the approaches TCUs employ to optimize shift changes:
- Comfort and smoothness: One of TCUs’ primary goals is to ensure that shift transitions are smooth and comfortable. Shifts that are sudden or jerky can cause driver discomfort and reduce vehicle durability. TCUs use algorithms to manage clutch engagement and disengagement, minimizing torque interruption during shifts, resulting in smooth shifts. This improves the driving experience by allowing for a smooth transfer of power from one gear to the next.
- Fuel efficiency: To maximize fuel efficiency, shift transitions must be effective. TCUs try to keep the engine as efficient as possible. Transmission Control Units help reduce unnecessary gear changes and improve fuel efficiency by selecting the proper gear.
- Performance: TCUs are vital for improving performance in sports cars. When accelerating, they can postpone upshifts to keep the engine in its power band, resulting in quick reaction and maximum power output. They also make it easy to downshift for passionate driving or quick overtakes, allowing the driver to take full advantage of the engine’s power.
- Adaptive Shifting: Many modern transmission control units feature adaptive shifting algorithms that take into account a wide range of variables, like driving behaviors, ambient conditions, and load situations. These algorithms adjust shift sequences dynamically to provide a more personalized driving experience. For example, if the driver is hauling a huge trailer, the TCU may stay in lower ratios for longer periods of time to maintain power and stability.
- Temperature Management: Extreme temperatures can have an impact on transmission performance. TCUs monitor the temperature of the transmission fluid and adjust the shift patterns accordingly. In hot weather, they may prioritize cooling by reducing torque load during shifts; in cold weather, they may delay upshifts to allow the transmission to warm up.
- Overcoming wear and tear: TCUs include diagnostic and preventive maintenance functions. They can detect wear and future faults in the transmission and adjust it accordingly. This proactive method can extend the transmission’s life and reduce repair costs.

Challenges and considerations:
TCUs have a lot to offer, but there are also some downsides.
- Complexity: As modern transmissions become more complex, advanced TCUs are required, making diagnosis and maintenance more difficult and expensive.
- Sensors and Data: Data collection by Transmission Control Units is heavily reliant on sensors. The sensitivity of these sensors to wear, damage, and environmental conditions may have an effect on TCU performance.
- Software upgrades: TCUs, like any other electronic system, may require software upgrades to address problems or improve performance. The bulk of the time, trained technicians must perform these updates.
- Integration: To work properly, TCUs must communicate with other vehicle systems, such as the engine control unit (ECU) and electronic stability control (ESC).

Conclusion:
The hidden heroes of modern vehicles are the transmission control units, which oversee seamless and effective gear shifts that improve driving comfort, fuel efficiency, and vehicle longevity. These sophisticated solutions optimize shift transitions based on several factors, constantly reacting to driver behavior and environmental conditions.
We should expect even more powerful transmission control units as automobile technology advances, possibly with AI and machine learning to improve shift transitions even further. The future of TCUs holds the promise of even more personalized and effective driving experiences, ensuring that every gear shift is as seamless and ideal as possible, whether you’re driving along the highway or pushing your limits on the racetrack.
“Experience Unmatched Reliability with Our Advanced VCUs!” Explore our best VCU-related products and services at Dorleco.com.

