Introduction
It’s important to understand the many kinds of electric vehicles available whether you’re thinking about buying an EV for the first time or upgrading your current one. The most crucial fact to be aware of is that there are two main types of electric cars: BEVs and PHEVs. We’ll go over the distinctions between the BEVs and PHEVs as well as the benefits and drawbacks of BEVs and PHEVs in this post.
What is a PHEV?
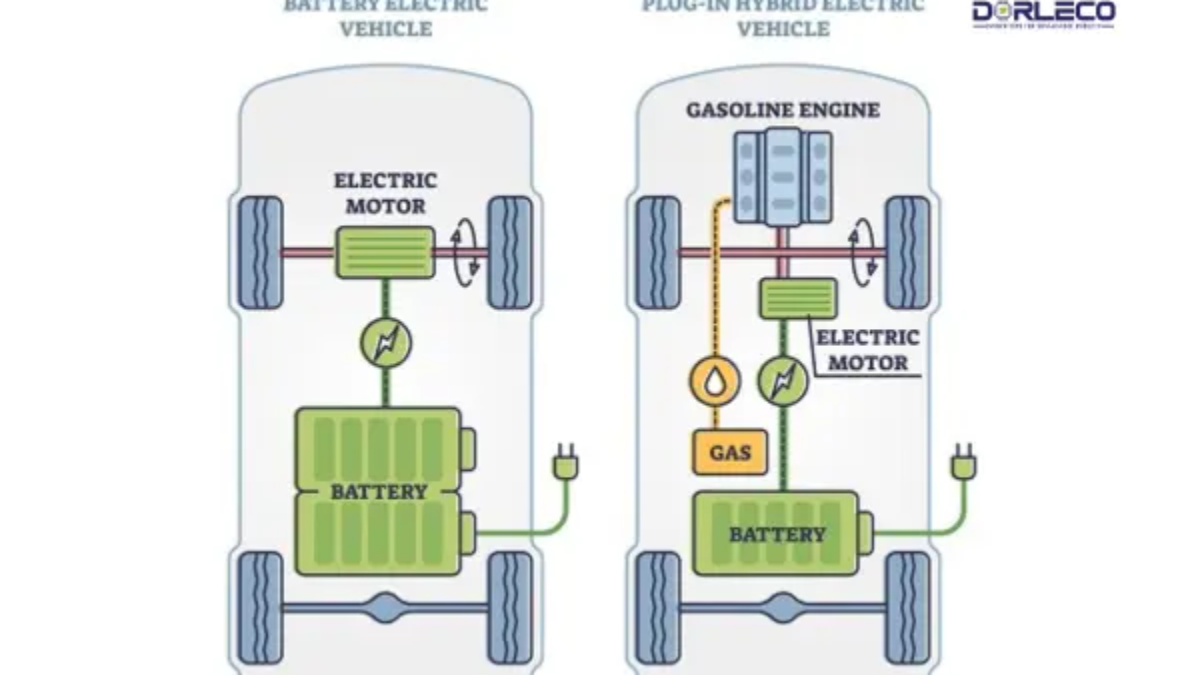
An electric motor and internal combustion engine work together to power hybrid cars. How does one define a hybrid? Conventional hybrids recharge using technologies like regenerative braking and interchangeably run on gas or electricity. A PHEV: What is it? A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle, or PHEV, is a car that runs entirely on electricity for short distances. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles require an additional power source, such as a home or public charging station, to recharge their larger and more powerful battery than a traditional hybrid.
In a PHEV, the gas-powered engine can function as a backup, taking over if the battery runs out of electricity. When comparing BEVs and PHEVs options, some St Louis Park drivers may experience range anxiety that this backup can help to ease.
What is a BEV?
Electricity is the only source of power for battery electric vehicles or BEVs. An internal combustion engine (ICE), a gasoline tank, and an exhaust pipe are absent from a BEV. Rather, it is equipped with one or more electric motors that are fueled by a larger battery that needs to be charged via an external outlet. More about the JuiceBox Level 2 Home charger, which is a strong charger that can fully charge your car overnight, is provided below.
If you want to completely stop using gasoline, a BEV is what you need. A BEV: What is it? A BEV is a battery-electric car that has a bigger motor and battery pack than a plug-in hybrid electric car (PHEV). The main distinction between a BEV and a PHEV is that the former runs exclusively on electricity and has no emissions. Among the advantages of electric vehicles are:
- Because electric automobiles don’t have exhaust systems, they produce no harmful emissions.
- Because a BEV doesn’t use engine oil, oil changes are not necessary.
- The absence of an internal combustion engine in an electric vehicle (EV) makes driving on the roads in and around Minneapolis quieter and more peaceful.
- On the highways in the Golden Valley area, you may still experience rapid acceleration because modern BEVs can produce torque almost instantly.
- Numerous BEV models qualify for a state or federal tax credit.
Benefits of a BEV
1. Simplicity
One of the main benefits of the BEV is its simplicity. A battery-electric vehicle requires very little maintenance because it has so few moving parts. Because there aren’t any other fluid changes or oil changes, like engine oil, a BEV only needs a few tune-ups. Just plug it in and get going!
2. Cost-savings
The savings from fewer maintenance costs can add up to a sizable sum throughout the vehicle’s lifetime. Additionally, compared to electric power, fuel costs are typically higher when utilizing a gas-powered combustion engine. The total cost of ownership for an electric automobile during its battery lifespan can be similar to, or even more expensive than, that of a BEV, depending on how the vehicle is used.
3. Benefits of Climate
You can be secure in the knowledge that you’re making a positive environmental impact by switching to electric vehicles from gas-powered ones. Along with harmful substances including nitrous oxides, volatile organic compounds, fine particulate matter, carbon monoxide, ozone, and lead, internal combustion engines emit CO2 emissions that warm the globe.
Over four times as efficient as gas-powered vehicles are electric vehicles. This is a significant benefit over conventional cars and saves about three tons of carbon dioxide emissions annually. Moreover, the grid, which is gradually transitioning to renewable energy sources, provides power for EVs.
Additionally, JuiceEco, which combines EV charging electricity use with zero-emission, 100% renewable energy, allows drivers of electric vehicles to further reduce their carbon footprint.
4. Fun
Riding a fully electric vehicle is undoubtedly enjoyable. People who own electric vehicles are rather pleased with them because of the quiet acceleration, the absence of foul-smelling tailpipe emissions, and the smooth steering. 96% of EV owners said they have no intention of switching back to gas.
Disadvantages of BEV
- Range Anxiety
- After a set number of kilometers, BEVs need to be recharged because of their limited operational range. For those who need to travel frequently or have lengthy travel plans, this could be a drawback.
- Inadequate Infrastructure for Charging
- Compared to gas stations, there are fewer BEV charging stations available.
- Therefore, if charging is not available at home or the workplace, owning a BEV may be difficult.
- Greater Starting Expense
- In general, BEVs are more expensive upfront than conventional cars.
Benefits of a PHEV
1. Up-front costs (for now)
Most of an electric car’s initial cost is related to its battery. PHEVs often have cheaper upfront expenses than BEVs since they have smaller batteries.
However, as previously indicated, a PHEV’s lifespan expenditures may increase due to the cost of gas, maintenance for its internal combustion engine, and other non-electric components.
The lifetime expenses will go down the more you drive electric; therefore, if your plug-in hybrid is fully charged and you typically take short journeys, you should be able to drive for extended periods without using gas.
The average driver travels 25.9 miles per day in their automobile, and 91% of all car trips are less than 20 miles, according to the most recent National Household Travel Survey.
The majority of PHEVs on the market can drive this distance on electricity. We anticipate that the initial costs of all-electric vehicles will decrease in the future as battery technology advances.
2. Flexibility
Although owners of plug-in hybrids will want to keep their batteries charged frequently to take advantage of the cost savings associated with using electricity, they are not obligated to do so to use the car.
If a plug-in hybrid isn’t charged from a wall outlet, it will function similarly to a traditional hybrid electric car. It is therefore not a problem if the owner drives to a place without access to an electric vehicle charger or forgets to plug the car in one day.
Because PHEVs often have a lower electric range, gas will be required. For certain drivers who might be nervous about charging their EV while driving or who have range anxiety, this is a benefit.
As more and more public charging stations become available, we expect that this will soon change. Of course, having a top-notch home charger will eliminate the need for you to worry about juicing while on the move!
3. Choice
PHEVs outnumber BEVs in the market at the moment. Thirty-two plug-in electric hybrid cars (PHEVs) were on the market in the United States as of September 4, 2021.
While Volvo and Audi each offer three PHEV vehicles, BMW offers five. There were 19 battery-electric car models and 26 total, including model variants, on the market in the United States as of January 9, 2021.
Among the firms selling BEVs are Ford Mustang, Tesla, and others.
4. Faster charging
The 120-volt level 1 charger that most battery electric cars come with is typical, however, it might take a very long time to fully charge the car.
This is so because battery-electric cars have considerably bigger batteries than plug-in hybrid electric vehicles. Of course, no matter what kind of electric vehicle you own, you can charge quickly if you have a strong, powerful charger like the Level 2 Juice Box!
Disadvantages of PHEVs
- Reduced Effectiveness
- PHEVs are less efficient than BEVs that only run on batteries since they require both gasoline and batteries.
- Increased Upkeep Expenses
- PHEVs require more maintenance than BEVs since they have more moving parts.
- Heavier and Less-streamlined Design
- PHEVs are heavier vehicles with a bulkier hybrid powertrain, giving them a less streamlined appearance.
CONCLUSION:
In conclusion, a comparison of BEVs and PHEVs demonstrates clear benefits and contrasts, with each vehicle type meeting a variety of demands and preferences in the field of electric transportation.
Because BEVs only run on electric batteries, they have no exhaust emissions, which makes them perfect for people who want to lessen their carbon footprint and for the environment.
Compared to PHEVs, they have a greater all-electric range, which makes them appropriate for shorter journeys and daily commutes without the need for gasoline.
Furthermore, because their drivetrains are simpler and have fewer moving parts, BEVs usually require less maintenance.
PHEVs, on the other hand, provide adaptability and do away with range anxiety by combining electric propulsion with an internal combustion engine.
They are more flexible to accommodate a greater variety of driving styles and lifestyles since they offer the comfort of gasoline for longer trips or in situations where charging infrastructure is scarce.
For people who are reluctant to switch entirely to electric vehicles, plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) provide a halfway ground between conventional and electric driving.
Though to differing degrees, BEVs and PHEVs both help to lower greenhouse gas emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.
The decision between the two is influenced by several variables, including driving habits, the accessibility of charging infrastructure, environmental considerations, and individual preferences.
The market for electric vehicles is constantly changing due to advancements in technology, infrastructure, and consumer demand.
This means that there are more options available and the viability of electric transportation as a sustainable alternative to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles is improving.
The basic objective of cutting carbon emissions and lessening environmental effects is still crucial in the shift to a greener and more sustainable future for transportation, regardless of whether a person chooses a BEV or PHEV.