Introduction
As the world gradually moves toward a greener and more sustainable future, VCUs in electric and hybrid vehicles have emerged as a potential means of combating climate change and reducing our dependency on fossil fuels. The Vehicle Control Unit (VCU) is a crucial component enabling the sophisticated technology that powers these state-of-the-art, environmentally friendly cars.
This blog explores the revolutionary effects, utility, and significance of VCUs on modern mobility, with particular reference to their application in electric and hybrid vehicles.
1. The Advancement of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles
Before we get into VCUs in Electric and Hybrid Vehicles, let’s take a quick look at the context in which these vehicles have gained popularity. Fears about pollution, climate change, and the depletion of fossil fuel resources have the auto industry searching for substitute propulsion methods. In terms of fuel efficiency and carbon emissions reduction, hybrid and electric vehicles present an alluring substitute for traditional internal combustion engine vehicles due to their ability to run on electricity.
2. Understanding the Vehicle Control Unit (VCU)
The brains of electric and hybrid cars are called vehicle control units, or VCUs. It is a powerful on-board computer that manages and arranges several essential functions to ensure a smooth and efficient driving experience. In addition to providing vital safety features, VCUs are crucial for maintaining battery health, optimizing energy consumption, and enhancing vehicle performance.
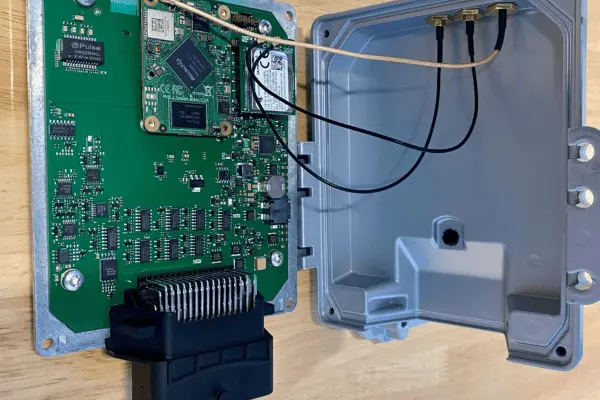
3. VCUs in Electric and Hybrid Vehicles: Features and Functions
- Battery Management System (BMS): One of the primary responsibilities of the VCU is to oversee the Battery Management System. Monitoring the battery’s voltage, temperature, and charge level is necessary to maintain optimal performance and avoid overcharging or discharging, which may reduce the battery pack’s lifespan.
- Powertrain Control: The energy flow from the battery to the internal combustion engine or electric motor is coordinated by the VCU, which also manages the powertrain. The management of torque, speed, and gear ratios is necessary to achieve optimal efficacy and performance.
- Regenerative Braking: VCUs enable regenerative braking, which is the process of recovering kinetic energy during braking and converting it back into electrical energy to recharge the battery. The car’s range is extended, and its total energy efficiency is raised.
- Driving Modes: VCUs offer a range of driving modes, such as eco, sport, and normal, allowing the user to adapt the vehicle’s performance to their preferences and road conditions.
- Fault Detection and Diagnostics: VCUs continuously scan various car parts, identifying issues or malfunctions and providing diagnostic information to the driver or maintenance personnel so they can take immediate action.
4. How VCUs Work in Autonomous Driving
As we get closer to fully autonomous vehicles, VCUs are essential to ensuring safety and enhancing autonomous driving abilities. VCUs analyze data from several sensors, like cameras, radar, and LiDAR, to give real-time information on the surroundings of the vehicle. This information is necessary to implement advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and make features like adaptive cruise control, automated emergency braking, and lane-keeping possible.

5. Improvements at VCUs
Adapt to changes in technology. The efficiency and functionality of VCUs in electric and hybrid vehicles are continuously being improved by manufacturers, allowing for smoother integration with other vehicle systems. Modern algorithms and artificial intelligence enable the capacity to learn from driving behaviors, maximize energy consumption, and personalize the driving experience.
The physical size and weight of these components are being decreased by VCU manufacturers to make these units lighter and more suited to different vehicle architectures. Integration with cloud services and vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) connectivity, which facilitates data exchange between automobiles and infrastructure for more intelligent mobility solutions, further improves VCU’s capabilities.
6. Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the tremendous developments in VCU technology, there are still many challenges. VCU interfaces and communication protocols need to be standardized to guarantee interoperability across different manufacturers and cars. Cyber security also becomes a big concern as VCUs control vital vehicle functions and handle sensitive data. Strong cyber security measures are necessary to defend against such threats.
Conclusion
VCUs in electric and hybrid vehicles have a bright future ahead of them. In the years to come, VCUs in electric and hybrid vehicles will be widely used due to the continuing advancements in energy efficiency, driving range, and safety regulations.
Although the technology for VCUs in electric and hybrid vehicles has advanced impressively, there are still certain issues to resolve. Standardization of VCU interfaces and communication protocols is required to guarantee interoperability with various car models and manufacturers. Cyber security is also a major issue because VCUs handle private information and regulate vital automotive systems. Strong cyber security measures must be put in place to thwart such threats.
VCUs have a bright future ahead of them in hybrid and electric cars. In the upcoming years, the broad adoption of VCUs in electric and hybrid vehicles will be facilitated by ongoing research and development that will raise safety requirements, driving range, and energy economy.
To review our excellent VCU products and services and to find out more about our software development capabilities for battery-specific applications, send an email to info@dorleco.com.